
What is your Response Time, Your Attention and Interference in the Reaction Time?
If conflicting signature problem occurs, uninstall your app and download the new version.
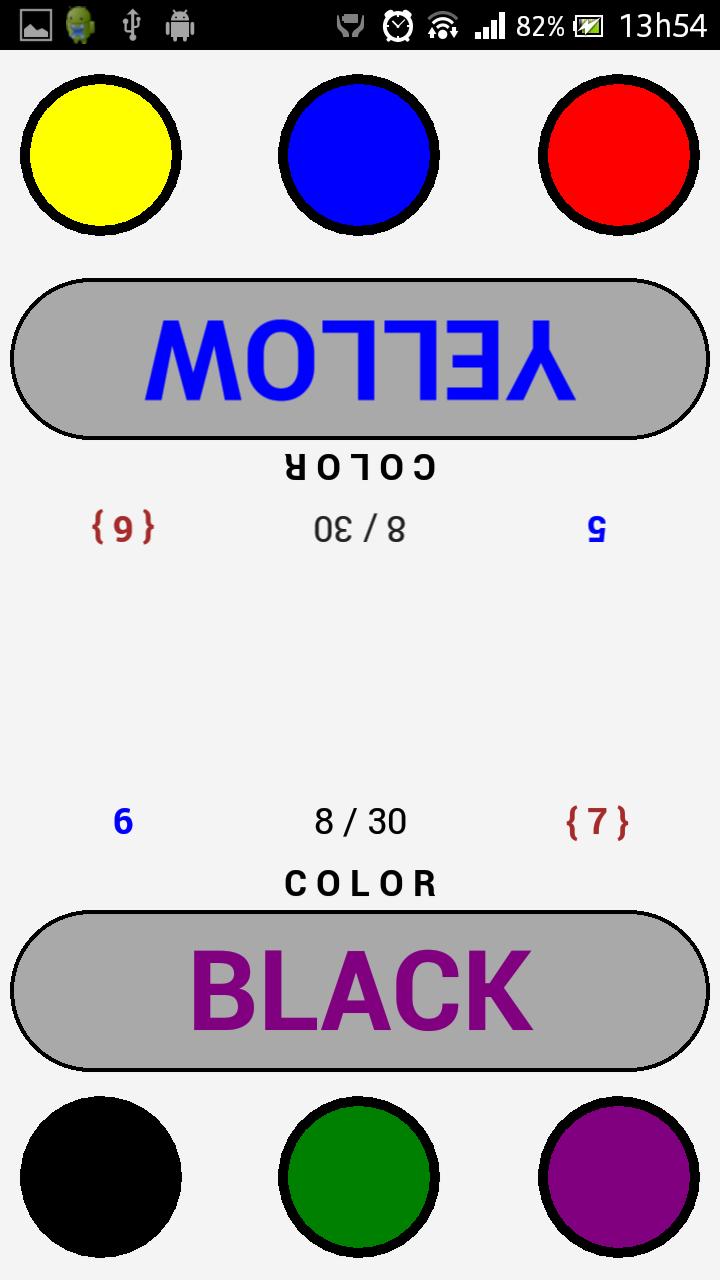
The Stroop test is the best and most customizable test of the genre.
Present in Brazil, United States, Spain, Italy, Mexico, Colombia, India, Canada, Indonesia, Greece, Argentina and many other countries.
Send your suggestion to [email protected].
The Stroop test is a form of software representation of the test created by John Ridley Stroop (1897 - 1973) who was an American psychologist whose research in cognition and interference continues to be considered by some as the gold standard in attention studies.
[Psychologist, psychiatrist or mental health professional]
Apply the test to your patients according to their practices and measure response time, attention capacity and interference at reaction time.
Learn more about the Stroop test by contacting the author ([email protected]).
Give your tips and suggestions or see about the development of your personalized program.
[The best and most customizable Stroop test]
With various test levels and two game levels*, applying the main concepts of the Stroop effect.
Available in Portuguese (BR), English and Spanish.
* All levels are available only in the full version.
Test levels
- Beginner
- Intermediary
- Advanced
- Senior
- [Random]
- [personalized]
Game levels
- [double beginner]
- [Senior double]
In psychology, the Stroop effect is a demonstration of interference in the reaction time of a task. The effect has been used to create a psychological test (Stroop test), which is widely used in clinical practice and research. The Stroop effect has been used to investigate a person's psychological abilities, as its discovery during the twentieth century has become a popular neuropsychological test.
In the first trial, the name of the written color is different from printed ink and the participant must say the written word. In the second experiment, the participant must name the color of the ink instead.
This test is considered to measure selective attention, cognitive flexibility and processing speed, and is used as a tool for evaluating executive functions. An increase in the effect of interference is found in disorders such as brain damage, dementia and neurodegenerative diseases, attention deficit, hyperactivity, schizophrenia, addictions and depression.